After this documentation was released in July 2003, I was approached
by Prentice Hall and asked to write a book on the Linux VM under the Bruce Peren's Open Book Series.
The book is available and called simply "Understanding The Linux Virtual
Memory Manager". There is a lot of additional material in the book that is
not available here, including details on later 2.4 kernels, introductions
to 2.6, a whole new chapter on the shared memory filesystem, coverage of TLB
management, a lot more code commentary, countless other additions and
clarifications and a CD with lots of cool stuff on it. This material (although
now dated and lacking in comparison to the book) will remain available
although I obviously encourge you to buy the book from your favourite book
store :-) . As the book is under the Bruce Perens Open Book Series, it will
be available 90 days after appearing on the book shelves which means it
is not available right now. When it is available, it will be downloadable
from http://www.phptr.com/perens
so check there for more information.
To be fully clear, this webpage is not the actual book.




Next: 5.3 Process Address Space
Up: 5. Process Address Space
Previous: 5.1 Linear Address Space
Contents
Index
The address space usable by the process is managed by a high level
mm_struct which is roughly analogous to the
vmspace struct in BSD [#!mckusick96!#].
Each address space consists of a number of page-aligned regions of memory
that are in use. They never overlap and represent a set of addresses
which contain pages that are related to each other in terms of protection
and purpose. These regions are represented by a struct
vm_area_struct and are roughly analogous to the
vm_map_entry struct in BSD. For clarity, a region may
represent the process heap for use with malloc(), a memory mapped
file such as a shared library or a block of anonymous memory allocated with
mmap(). The pages for this region may still have to be allocated,
be active and resident or have been paged out.
If a region is backed by a file, its
vm_file field will be set. By traversing
vm_file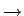 f_dentry
f_dentry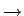 d_inode
d_inode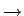 i_mapping,
the associated address_space for the region may be
obtained. The address_space has all the filesystem specific
information required to perform page-based operations on disk.
i_mapping,
the associated address_space for the region may be
obtained. The address_space has all the filesystem specific
information required to perform page-based operations on disk.
A number of system calls are provided which affect the address space and
regions. These are listed in Table 5.1
Table 5.1:
System Calls Related to Memory Regions
 |




Next: 5.3 Process Address Space
Up: 5. Process Address Space
Previous: 5.1 Linear Address Space
Contents
Index
Mel
2004-02-15
![]() f_dentry
f_dentry![]() d_inode
d_inode![]() i_mapping,
the associated address_space for the region may be
obtained. The address_space has all the filesystem specific
information required to perform page-based operations on disk.
i_mapping,
the associated address_space for the region may be
obtained. The address_space has all the filesystem specific
information required to perform page-based operations on disk.